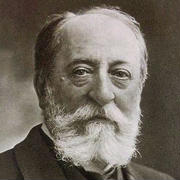Gabriel Urbain Fauré (French: [ɡabʁiɛl yʁbɛ̃ fɔʁe]; 12 May 1845 – 4 November 1924) was a French composer, organist, pianist and teacher. He was one of the foremost French composers of his generation, and his musical style influenced many 20th-century composers. Among his best-known works are his Pavane, Requiem, Sicilienne, nocturnes for piano and the songs "Après un rêve" and "Clair de lune". Although his best-known and most accessible compositions are generally his earlier ones, Fauré composed many of his most highly regarded works in his later years, in a more harmonically and melodically complex style.
Fauré was born into a cultured but not especially musical family. His talent became clear when he was a small boy. At the age of nine, he was sent to the Ecole Niedermeyer music college in Paris, where he was trained to be a church organist and choirmaster. Among his teachers was Camille Saint-Saëns, who became a lifelong friend. After graduating from the college in 1865, Fauré earned a modest living as an organist and teacher, leaving him little time for composition. When he became successful in his middle age, holding the important posts of organist of the Église de la Madeleine and director of the Paris Conservatoire, he still lacked time for composing; he retreated to the countryside in the summer holidays to concentrate on composition. By his last years, Fauré was recognised in France as the leading French composer of his day. An unprecedented national musical tribute was held for him in Paris in 1922, headed by the president of the French Republic. Outside France, Fauré's music took decades to become widely accepted, except in Britain, where he had many admirers during his lifetime.
Fauré's music has been described as linking the end of Romanticism with the modernism of the second quarter of the 20th century. When he was born, Chopin was still composing, and by the time of Fauré's death, jazz and the atonal music of the Second Viennese School were being heard. The Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians, which describes him as the most advanced composer of his generation in France, notes that his harmonic and melodic innovations influenced the teaching of harmony for later generations. During the last twenty years of his life, he suffered from increasing deafness. In contrast with the charm of his earlier music, his works from this period are sometimes elusive and withdrawn in character, and at other times turbulent and impassioned.
Cite error: There are <ref group=n> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=n}} template (see the help page).