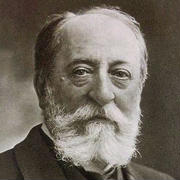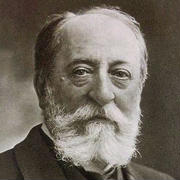Joseph Maurice Ravel (7 March 1875 – 28 December 1937) was a French composer, pianist and conductor. He is often associated with impressionism along with his elder contemporary Claude Debussy, although both composers rejected the term. In the 1920s and 1930s Ravel was internationally regarded as France's greatest living composer.
Born to a music-loving family, Ravel attended France's premier music college, the Paris Conservatoire; he was not well regarded by its conservative establishment, whose biased treatment of him caused a scandal. After leaving the conservatoire, Ravel found his own way as a composer, developing a style of great clarity and incorporating elements of modernism, baroque, neoclassicism and, in his later works, jazz. He liked to experiment with musical form, as in his best-known work, Boléro (1928), in which repetition takes the place of development. Renowned for his abilities in orchestration, Ravel made some orchestral arrangements of other composers' piano music, of which his 1922 version of Mussorgsky's Pictures at an Exhibition is the best known.
A slow and painstaking worker, Ravel composed fewer pieces than many of his contemporaries. Among his works to enter the repertoire are pieces for piano, chamber music, two piano concertos, ballet music, two operas and eight song cycles; he wrote no symphonies or church music. Many of his works exist in two versions: first, a piano score and later an orchestration. Some of his piano music, such as Gaspard de la nuit (1908), is exceptionally difficult to play, and his complex orchestral works such as Daphnis et Chloé (1912) require skilful balance in performance.
Ravel was among the first composers to recognise the potential of recording to bring their music to a wider public. From the 1920s, despite limited technique as a pianist or conductor, he took part in recordings of several of his works; others were made under his supervision.
Cite error: There are <ref group=n> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=n}} template (see the help page).